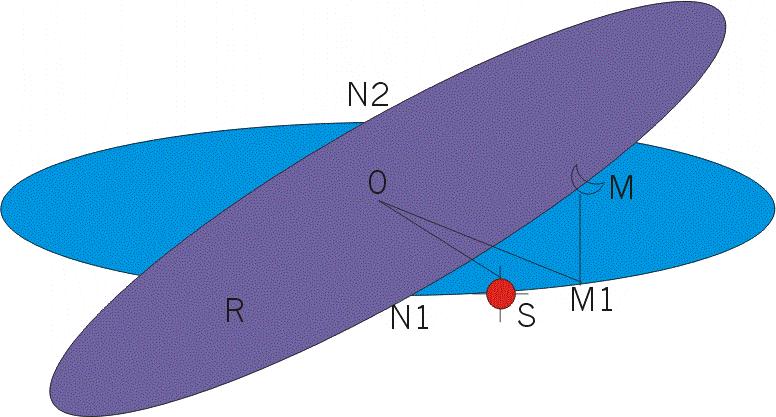
To know more about eclipses, we need to understand more about the moon's motion. We know that the moon, like the other heavenly bodies, lies in the celestial sphere. The path traced out by the moon, during its motion, forms a circle in celestial sphere. This circle is inclined at an angle of 5.2° to the ecliptic. Take a look at the figure below.

From the figure, we can observe that the moon does not move along the ecliptic. Since the circular path of the moon and the plane containing the ecliptic are inclined at an angle, they intersect each other at two points N1 and N2. These two points are called as the Nodes of the moon's orbit. These nodes are shown in the figure.
When the moon is at either of the nodes, it is in the plane containing the ecliptic. Only when the moon is at either of the points N1 or N2, can an eclipse occur. Why is it so? Recall that, for an eclipse to occur, the earth, the sun and the moon should lie in a single straight line. The sun will always lie in the ecliptic. If the moon should be in the line joining the sun and the earth, it can't be in any position other than the two nodes. Will an eclipse always occur if the moon is in the nodes? No. Even when the moon is at one of the nodes, the sun can be in any other position so that the sun, the earth and the moon do not form part of a single straight line.
Now, why is that you do not get eclipses during every full moon day or new moon day? You see, this is because of the fact that the moon is not located at either of the nodes during every full moon or new moon day. That is why there aren't eclipses on all full moon and new moon days. More details about the nodes